If you are learning about the virtual currency Bitcoin, this article will help you understand it better. Bitcoin is a type of digital currency created in 2009 and used worldwide. In this article, we will explore how Bitcoin works, its history, and its applications.
Table of Contents
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a type of digital currency created in 2009 by a person or a group of people using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. The most significant difference between Bitcoin and traditional currencies is that it is not regulated by any organization or government in the world. Instead, Bitcoin is managed by a global network of users.
A total of 21,000,000 BTC have been created. By January 2023, 19.2 million BTC had been mined, leaving 1.8 million BTC yet to be mined.
The Development History of Bitcoin
Bitcoin was created in 2009 by a person or a group of people using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. However, the founder of Bitcoin has not been officially identified. In the early years, Bitcoin was not widely known and was used only by a few tech enthusiasts. However, since 2017, the value of Bitcoin has skyrocketed, attracting the attention of many investors and users worldwide. Today, Bitcoin is the most famous virtual currency in the world and is widely used in online transactions.
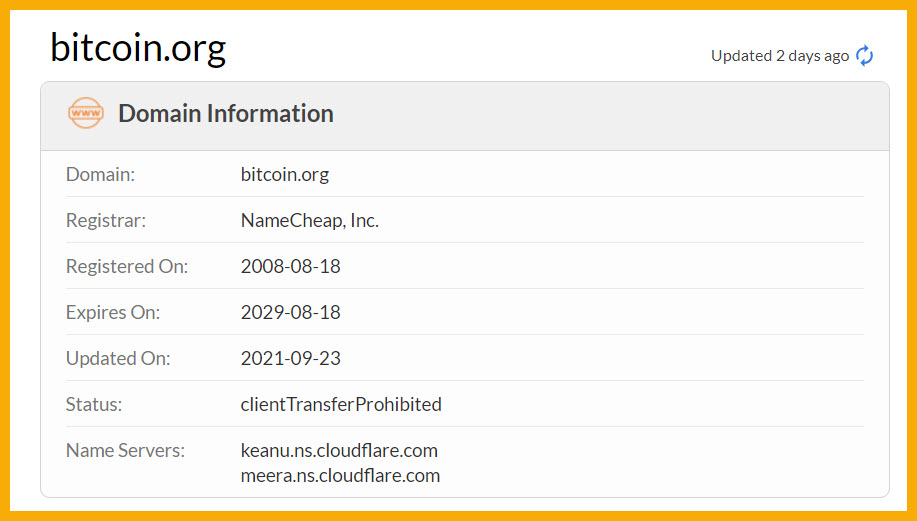
The domain bitcoin.org was registered on August 18, 2008.
Bitcoin was first mentioned on October 31, 2008, in the white paper about the peer-to-peer payment protocol by the anonymous figure Satoshi Nakamoto. It began to be used from January 9, 2009, with the original Bitcoin block (Genesis Block). The following text was embedded in the content of the Genesis Block:
The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks” – This is a reference to an article from The Times of London indicating that the UK government had failed to stimulate the economy and was preparing to issue a second bailout package for the banks, caused by the fractional-reserve banking system.
The first Bitcoin transaction was made when Satoshi Nakamoto sent 10 bitcoins to cryptographer Hal Finney on January 12, 2009, shortly after the Bitcoin software was first released.
On October 5, 2009, New Liberty Standard established the initial exchange rate for Bitcoin, where 1 dollar was equivalent to 1,309.03 Bitcoins (or 1 Bitcoin = 0.00076 USD). This value was calculated based on the electricity cost of a computer required to mine Bitcoin.
Bitcoin Milestones
- 2007: Nakamoto Satoshi begins working on the idea.
- August 2008: Bitcoin.org is registered – This was once a forum for the entire crypto market where the community discussed not only crypto but also other projects – similar to Twitter today.
- October 2008: Bitcoin Whitepaper is published.
- January 2009: The first Bitcoin transaction is made at block #170.
- May 2010: The first real-world transaction is conducted, exchanging 10,000 BTC for pizza. Since then, the crypto market celebrates “Pizza Day” to commemorate the “super expensive” pizza!
- July 2010: Mt. Gox is established. This was once the largest exchange, making it easier to buy and sell BTC. However, the hack of Mt. Gox shocked the market.
- 2011: Blockchain.com is founded, serving as a leading Blockchain explorer and Bitcoin wallet at that time.
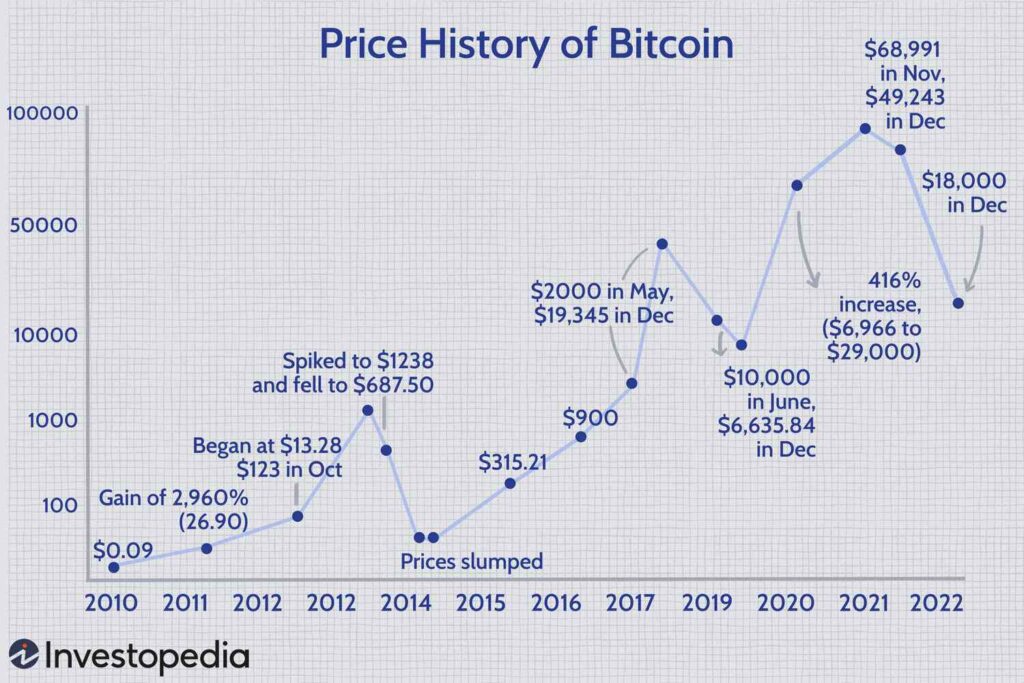
- March 2011: Bitcoin reaches $1 for the first time.
- June 2012: Coinbase is established – initially developing a Bitcoin wallet and later expanding into an exchange, becoming the first cryptocurrency exchange to IPO on the US stock market.
- May 2013: The first Bitcoin ATM is launched in San Diego, USA. Today, Bitcoin ATMs are present in many countries, including Vietnam.
- December 2013: Bitcoin reaches $1,000 for the first time, with a market capitalization of $13 billion.
- August 2017: Bitcoin forks into two chains: Bitcoin (BTC) and Bitcoin Cash (BCH).
- September 2017: JP Morgan calls Bitcoin a potential fraud, but later they issue products related to Bitcoin.
- December 2017: Bitcoin peaks at $19,400, with a market cap of $320 billion.
- March 2021: Tesla announces the purchase of Bitcoin and allows the purchase of cars using Bitcoin.
- June 2021: El Salvador becomes the first country to accept Bitcoin as legal tender.
- October 2021: Bitcoin peaks at $67,000, with a market cap of $1.26 trillion.
- November 2021: Bitcoin successfully updates the Taproot soft fork.
Although Bitcoin is not as widely used as some other coins in the DeFi market, it remains the most capitalized cryptocurrency and is increasingly accepted by many tycoons, states, and financial institutions.
How Bitcoin Works
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that securely records and verifies transactions across multiple computers or nodes. Initially introduced as the underlying technology behind the cryptocurrency Bitcoin, it has since been recognized for its potential applications beyond digital currencies.
At its core, a blockchain is a continuously growing list of records, called blocks, which are linked using cryptographic hashes to form a chain. Each block contains a set of transactions or data, along with a reference to the previous block. This structure ensures the integrity and immutability of the data recorded on the blockchain.
The decentralized nature of blockchain means that no central authority or intermediary controls the system. Instead, transactions and data are validated and verified by a network of participants, often referred to as nodes or miners. These participants collectively maintain the security of the blockchain, ensuring consensus on the ledger’s state.
Blockchain technology offers several key features and benefits:
- Transparency: The distributed nature of blockchain allows all participants to access the same information, promoting transparency and reducing the need for trust between parties.
- Security: The use of cryptographic algorithms and consensus mechanisms makes blockchain highly secure against tampering and fraud. Once a block is added to the chain, altering its content becomes extremely difficult.
- Immutability: Data stored on the blockchain is resistant to modification, ensuring the integrity of transactions and records.
- Decentralization: Blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network, eliminating the need for intermediaries and enabling direct transactions between participants.
- Trustless: Blockchain allows participants to interact and transact without relying on a central authority or third-party trust. Instead, trust is placed in the mathematical and cryptographic principles underpinning the technology.
- Smart Contracts: Blockchain can support the execution of self-executing contracts known as smart contracts. These contracts automatically perform predefined actions when specific conditions are met, further enhancing transaction efficiency and automation.
Blockchain technology has expanded beyond cryptocurrencies, finding applications in various industries such as finance, supply chain management, healthcare, voting systems, and more. It has the potential to revolutionize traditional systems by increasing transparency, reducing costs, enhancing security, and streamlining processes.
Benefits and Risks of Using Bitcoin
Using Bitcoin offers numerous benefits, including high security and safety, global availability, and freedom from control by any organization or government. However, there are also risks associated with Bitcoin usage, such as price volatility, the risk of losing money due to technical errors or hacking, and the potential use of Bitcoin for illegal activities. If you decide to use Bitcoin, make sure you understand the risks and have plans to mitigate them.
How to Buy and Sell Bitcoin
To buy and sell Bitcoin, you need to find a reliable Bitcoin exchange. These exchanges allow you to buy and sell Bitcoin with various currencies, such as USD or EUR. You can also buy Bitcoin from direct sellers through websites like Remitano. However, remember that the value of Bitcoin can change rapidly, so ensure you understand the risks before buying and selling Bitcoin.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency created in 2009 by an unknown person or group of people using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. It operates on a peer-to-peer network, allowing users to send and receive payments without the need for intermediaries like banks or governments.
2. How does Bitcoin work?
Bitcoin transactions are recorded on a public ledger called the blockchain, which is maintained by a network of computers known as nodes. Transactions are verified and confirmed by miners, who use computational power to solve complex mathematical puzzles. Once a transaction is confirmed, it is added to a block and appended to the blockchain.
3. What is blockchain?
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that securely records and verifies transactions across multiple computers or nodes. Each block in the blockchain contains a set of transactions, along with a reference to the previous block, creating a chain of blocks. Blockchain technology ensures transparency, security, and immutability of data.
4. Is Bitcoin legal?
The legality of Bitcoin varies from country to country. While some countries have embraced Bitcoin and enacted regulations to govern its use, others have imposed restrictions or outright bans on cryptocurrency activities. It’s essential to familiarize yourself with the laws and regulations in your jurisdiction before buying or using Bitcoin.
5. How can I buy Bitcoin?
You can buy Bitcoin from cryptocurrency exchanges, peer-to-peer platforms, Bitcoin ATMs, or directly from individuals. To purchase Bitcoin, you’ll need to create an account on a reputable exchange, deposit funds, and place an order to buy Bitcoin at the current market price.
6. Can I mine Bitcoin?
Yes, you can mine Bitcoin by participating in the process of verifying and adding transactions to the blockchain. However, Bitcoin mining requires specialized hardware and consumes a significant amount of electricity. As the Bitcoin network becomes more competitive, mining profitability may vary, and it may not be feasible for everyone to mine Bitcoin.
7. Is Bitcoin anonymous?
While Bitcoin transactions are pseudonymous, meaning they are not directly tied to a person’s identity, they are recorded on the public blockchain, which can be viewed by anyone. With the right tools and techniques, it may be possible to trace Bitcoin transactions back to their owners. However, users can enhance their privacy by using techniques like mixing services or privacy-focused cryptocurrencies.
8. What are the risks of using Bitcoin?
Using Bitcoin carries several risks, including price volatility, security vulnerabilities, regulatory uncertainty, and the potential for loss due to human error or hacking. Additionally, Bitcoin transactions cannot be reversed, so if you send Bitcoin to the wrong address or fall victim to a scam, it may be challenging to recover your funds.
9. Can I use Bitcoin for illegal activities?
While Bitcoin itself is not illegal, it has been used for illicit purposes due to its pseudonymous nature and decentralized structure. However, the vast majority of Bitcoin transactions are legitimate, and many reputable businesses and organizations accept Bitcoin as a form of payment. It’s essential to use Bitcoin responsibly and comply with applicable laws and regulations.
10. Is Bitcoin the only cryptocurrency?
No, Bitcoin is just one of thousands of cryptocurrencies available today. While Bitcoin remains the most well-known and widely adopted cryptocurrency, there are many alternative cryptocurrencies, often referred to as altcoins, with different features, use cases, and underlying technologies.
These are some of the most frequently asked questions about Bitcoin. If you have any further inquiries, feel free to reach out to us.
Tài liệu tham khảo:

Comments (No)